|
Włodzisław Duch |
 |
|
Włodzisław Duch |
 |
Understanding mind/brain: the final frontier.
Ghosts are things of the past.
Mind is what the brain does.
Dualism is dead (literarily).
Brain research, behavioral neurophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, psycho-neuro-immuno-logy ... many fields
coming together.
Can we understand the brain? Can we understand H2 ?
Types of questions:

Sociobiology, Evolutionary Psychology, Evolutionary Medicine ...
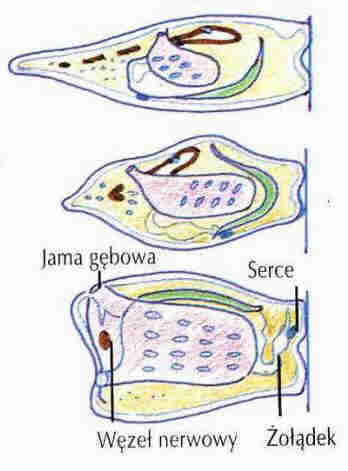
| Why do we have brains? | 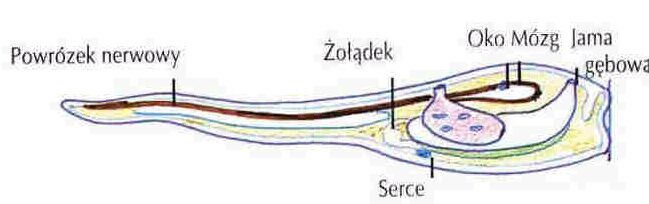 |
| To control movement!
Some see creatures eat their brains when they stop moving! |
 |
| Why left-right crossing in brain control? | 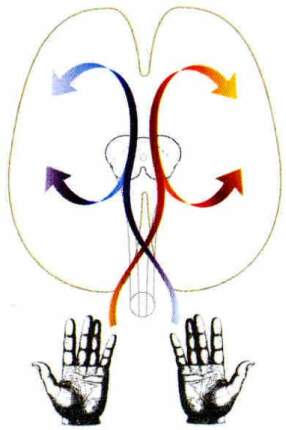 |
| Brain developed from ganglia in multi-segment worms which have a coil response. | 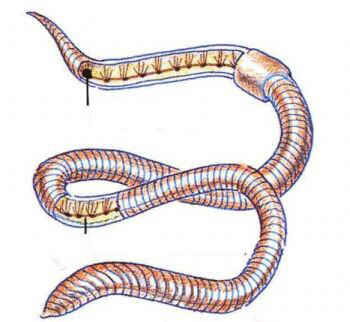 |
|
Igbo West African cultures raise yam plants and harvest it at the beginning of the rainy season.
Religious taboo: yam feast at the end of the rainy season, despite shortage of food. Why? Rainy season: mosquitoes spread malaria; many people have sickle cell anemia, a genetic disorder; become more resistant to malaria; yams contain a compound that combats the sickling of red blood cells. |
 |
|
Each level allows to answer specific "how" questions.
Brain imaging techniques: MRI, fMRI, EEG, MEG, SPECT, combinations.
|
 |
Information flow and analysis explains many amazing phenomena.
Some neuroanatomy.
|
Triune brain: archipalium (reptilian brain), paleopalium (mammal brain), neopallium (rational brain) |
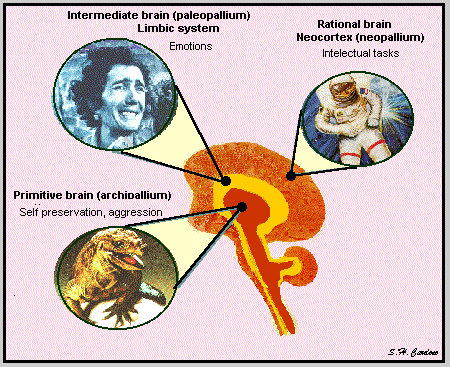 |
| Divided brain: hemispheres and specialization.
"Dominant" hemisphere (usually left): language, speech understanding, reading, logical thinking, internal
narration and dialog, precise and analytic, conscious.
In normal brain strong interhemispheric cooperation. Some differences between men-woman, ideographic-alphabetic writing users. |
 |
Neocortex - about 1010 neurons in many specialized areas, about 1014 connections.
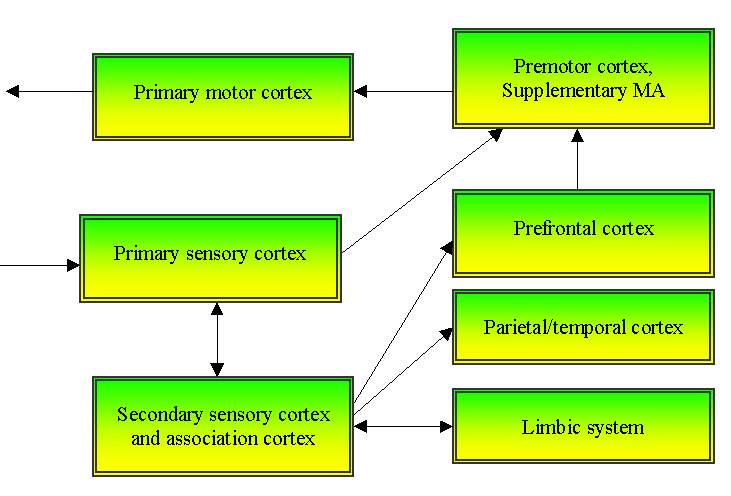
3 basic functions of the cortex:
Sensory analysis: primary, secondary (association), tertiary (multimodal) areas.
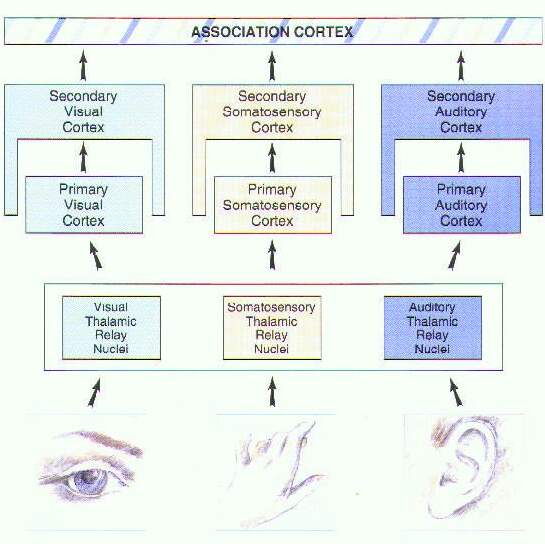
Motor control: primary, secondary areas + cerebellum - ca. 3 x 1010 neurons but only about 10
13 connections.
Association cortex - prefrontal, parietal, various gyri.
Brain lobes, 4 views: lateral, dorsal, medial and basal.
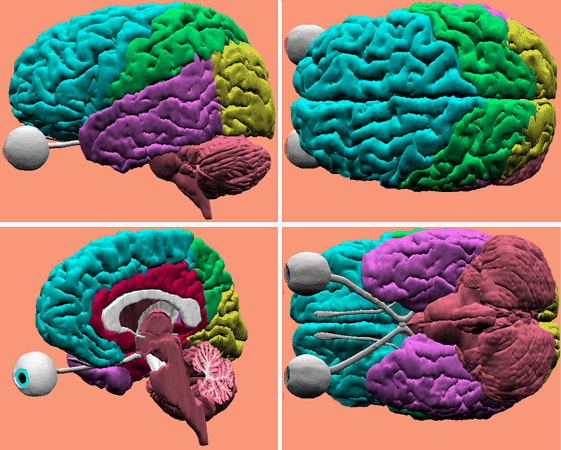
BrainlobesX, lateral lobes movie.
Brainlobesmid medial lobes movie.
Planum temporale movie.
Each gyrus (or part) has specific function (sometimes several functions).
Two basic mechanisms: topographical maps and population coding.
Sensory analysis: reduce input dimensionality, preserve topographical relations.
Somatosensory, motor, tonotopic, visual maps; maps also in cerebellum, thalamus and other subcortical
structures.
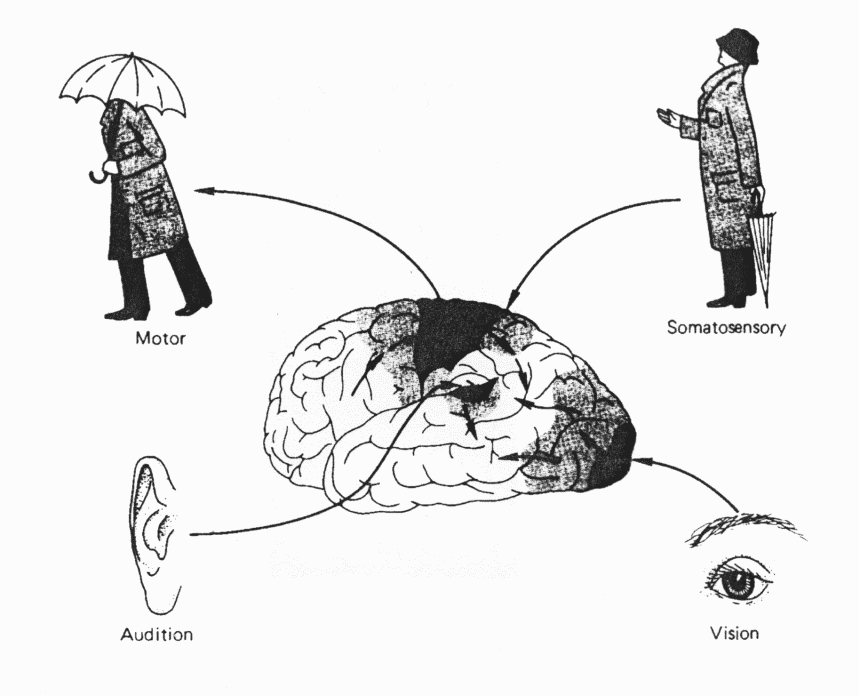
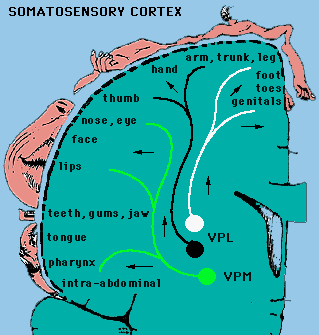
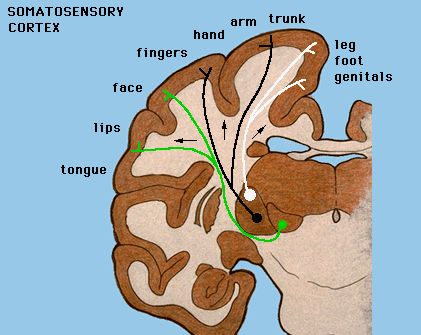
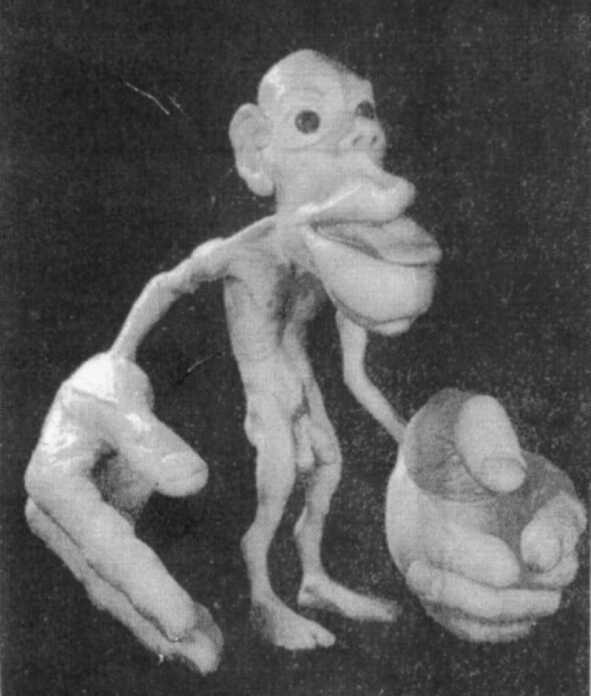
Somatosensory topographic maps in postcentral gyrus.
Somatosensory radiation movie.
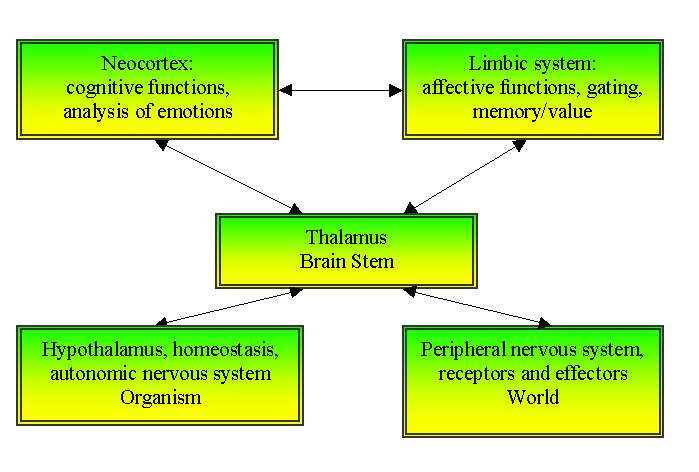
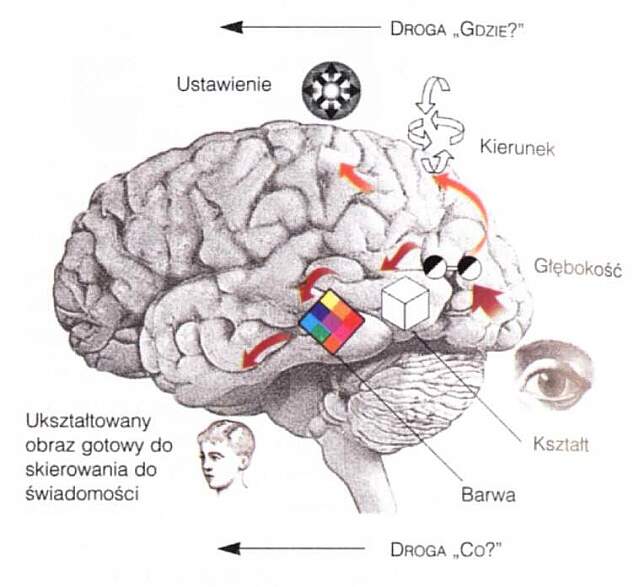
Recognition: fast thalamo-limbical route and slower cortical, ventral (object recogniton) and dorsal (movement,
action) streams.
VPL=Ventral Posterior Lateral Nucleus
VPM = Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus

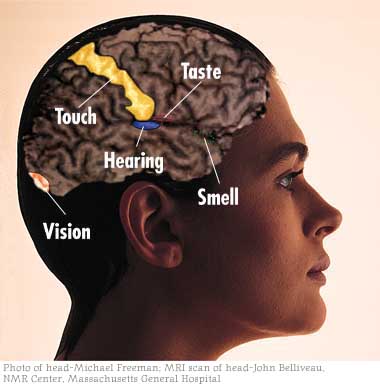
Each of the 6 senses has its cortex, primary and association.
|
Optic radiation movie.
|
|